The Move into Irrealism and How to Counter-Act It By Otto Laske The signs of a mutation of human consciousness since 2000 are becoming more and more clear: The real world disappears behind subjective screens propped up by objective social forces seeking profit. What the profit is meant to be used for is less than clear, and one can fear that it will serve psychological immaturity. The fact that consciousness overlays “itself” with screens signals a shift in the relationship in which empirical, actual, and real world are seen. Ontology, almost forgotten, is clubbed over the head once more. The disdain for empirical data, long in coming, and visible in the denial of global warming as well as integral speculation, seems to gain a stronger and stronger foothold. In Twitter, the links to the network of screens become shorter, and what was already short, like attention, is further shortened. What are the social consequences of this trend? Piaget thought of adult development as an increasing move out of ego-centrism, that is, the focus on “my little personality”. This hypothesis, followed in empirical research into the evolving self, is still on target, but the people using it are no dialectical thinkers.... Read More...
Category: Courses
Introduction to Dialectical Thinking
5' Introductory video: Otto Laske on the transformative power of learning dialectical thinking Read More...
Introduction to the three CDF Dimensions (Self-Study)
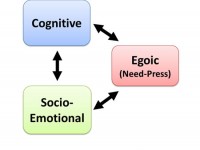
This course introduces students to a widely acclaimed, holistic perspective on both individuals and teams. It is an overview course focused the three perspectives in which CDF-users view clients: the social-emotional, cognitive, and psychological one. Insight into these dimensions stems from decades of validated research since the 1970s but has not been widely taught in a unified fashion. In the course, emphasis is placed as well on the interrelationships between the three dimensions since they closely interact in coaching as well as consulting. Based on this course, students become eligible for all other CDF courses. Read more Read More...
Introduction to Developmental Work with Teams
This course introduces team leaders and team coaches to fundamentally new ways of understanding the nature and behavior of teams, with the goal of re-shaping team dynamics. In the course, two main processes are distinguished: interpersonal and task process. Their balance is thought to define team maturity. The purpose of the course is twofold: to change coaches’ perception of teams based on social-emotional insight, and to give them new, dialectical, dialog tools for supporting team members’ interpersonal process and for strengthening their task process. Team maturity and different modes of team leadership are central course topics. The methodology taught goes far beyond purely the behavioral approaches now used, focusing on team members’ developmentally shaped frame of reference on account of which they collaborate in the team and view the organization they art part of the way they do. Students will be asked to submit a concise description of a team they are working with; their descriptions will provide the focus around which CDF tools are introduced and practiced in class. The study cohort itself will serve as a team to practice on. Read more Read More...
Socio-Emotional Development
The essence of the socio-emotional dimension has to do with how adults differ in making meaning of their life and work experiences based on their opposing and intertwined needs of being autonomous and being included in a community of others. These two lifelong tendencies achieve a different balance at every developmental “stage”. Social-emotional differences between people manifest not only in their “thinking”, but since thinking precedes acting, also in their goal setting, decision making, and, most directly, in the relationships individuals develop with others. In this life-changing course, students learn in depth not only the theory of social-emotional meaning making as developed by the Kohlberg School at Harvard, but acquire the practical skills of using what they learn, whether in making cogent assessments, giving cogent feedback, coaching, or consulting. Read More...
Cognitive Development Toward Dialectic
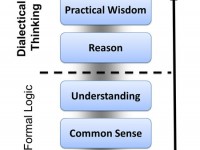
The essence of the cognitive dimension of CDF has to do with how adults differ in making cognitive sense (rather than meaning) of their life and work experiences, thus with what they do and do not understand about the real world. These differences go far beyond “what is in the head” since how people construct the world conceptually precedes their actions in the world, and thus equally manifests in their activities, planning, goal setting, decision making, and execution of leadership functions. In most general terms, students learn to switch from “what” to think to “how” to think, thereby gaining fluidity of thinking based on an awareness of their present way of thinking that makes some things “unthinkable” to them. In this life-changing course, students gain insight not only into the theory of cognitive development and the development of dialectic, but also begin to apply dialectical thought forms in text analysis, in cohort discussion, and in coaching interventions with individuals and teams. Read more Read More...