As shown at and, on this website, at , a workshop on new dialog methods specifically for creating collaborative intelligence in teams will take place in Milano, Italy, on January 30-31,2018. The workshop is offered by Consulenza Evolutiva, Milano and its Altroove School, and staffed by Lorenzo Campese, Alessandro Rossi, and Otto Laske. The workshop is a pioneering first in that it introduces Broad-Spectrum Systems Constellations which broaden the focus of attention of conventional constellations as detailed in the attached pdf. The workshop is held both in Italian and English. Those interested in signing up for the workshop with Consulenza Evolutiva will find further details on the workshop process below. Broad-Spectrum Systems Constellations Read More...
Category: Team Development
Thought Form Constellations as Measures of Team Connectivity
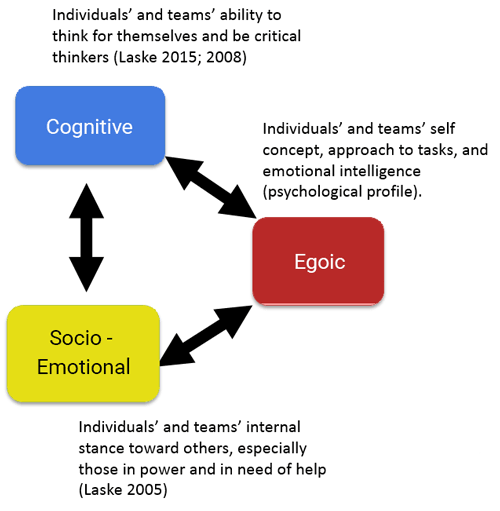
In this article, the author proposes structural, rather than behavioral or emotional, measures of team connectivity and introduces the notion of "cognitive" or "structural" systems constellations. These measures are derived from DTF, his Dialectical Thought Framework, a methodology rooted in cognitive developmental research since 1975. In contrast to the contemporary team literature, and in a follow up of an article co-authored with Graham Boyd on Distributed Leadership found in a book forthcoming at Palmgrave Publishers, UK, (#aboutBook), the author focuses on measuring team connectivity based on a team's cognitive behavior graph in real time. The author teaches DTF to both individuals, especially as coaches, and teams, in hands-on workshops in English and German, and with the help of a translator also in Spanish and Italian. TF Constellations 2 Read More...
Improving Management by Design: Novel Tools for Expanding and Deepening the Business Model Design Space
I propose to strengthen the cognitive processes involved in design thinking, especially for cross-functional teams, both through artificial intelligence techniques and focused cognitive coaching. I take as an example of design thinking the canvas metaphor used by Osterwalder and Pigneur (2014, 2010), selecting its CS (customer segment) component for further scrutiny. Specifically, I introduce an amplified form of design thinking called "transformational" thinking that is grounded in research in adult cognitive development over the lifespan (Laske 2008 [2017b/c]). My approach is rooted in DTF, the Dialectical Thought Form Framework developed at the Interdevelopmental Institute (IDM) since the year 2000. In focus in the blog is the notion of “hidden dimensions” of the canvas that iterative cognitive sprints of a cross-functional team reveal. I see such sprints as based on a combination of “breadth-first” and “depth-first” search, where the former is focused on creating the biggest possible picture, while the second deepens and refines the picture in its details, both in terms of thinking and resulting outcome. I show that the two kinds of searches are mutually reinforcing and that purely logical thinking (and thus algorithmic thinking also) fail in depth-first search, At the end of the text, I demonstrate by... Read More...
A methodology for creating a developmentally aware society
Until quite recently, the notion that adults develop over their entire lifetime has been a well kept academic secret. It still is. Attempts at establishing “deliberately developmental organizations” (DDO’s; Kegan & Lahey 2016), based on 40 years of research in adult development, are quite recent. This article introduces to the Constructive Developmental Framework (CDF), a synthesis of adult-developmental research since 1975 that has been taught as well as practiced at the Interdevelopmental Institute since 2000 (). CDF is a new tool for understanding how people experience life and work, mostly without full consciousness. This qualitative understanding emerges from semi-structured 1-hour interviews which shed new light on how people construct their workplace internally, both individually and in teams. CDFs main strength in business lies in providing new tools for boosting, through dialog, two human capabilities: making meaning of experiences (called “social-emotional”) and making sense of the real world conceptually (referred to as “cognitive”), as further explained below. Viewed more broadly, CDF comprises a political dimension as well. It is a framework for coaching for society, in the sense of developing self-authoring citizens who can think independently, rather than in dependence on internalized or external others. At the present time, where algorithms... Read More...
Transforming culture by transforming dialog in organizations and institutions
This short text explains what is important about crafting new forms of dialog in organizations and institutions seeking to be innovative. The text points to DTF, the Dialectical Thought Form Framework (2008, second edition 2017), that was introduced in a previous post entitled “A new approach to dialog.” In a time of deliberately developmental organization and organizations transcending rigid managerial hierarchies, the dialogical approach to thinking and managing here highlighted becomes an essential part of innovation. Short Preface, A new approach to dialog OL 3-2017 Read More...
A New Approach to Dialog: Teaching the Dialectical Thought Form Framework (DTF)
Can you imagine being part of a dialog in which you not only listen to what your interlocutor is saying but also to the underlying structure of his or her thinking? If you had knowledge of the thought form structure of human sense making, this way of listening, called “dialectical”, would enable you to point to what is missing (absent) both in your own and others’ verbal communication. It would thereby help you deepen your and others' thinking in real-time dialog. Your critical listening would then not be restricted to content but would equally focus on underlying thought structures used by your interlocutors. In a team and group context, you would be able to point to interlocutors’ thought gaps in a compassionate, inter-developmental, way. Such gaps are not “academic”. They are more serious than that since they translate into gaps between how people think and how reality works. It is this kind of dialog that the present article introduces. The article paves the way for an intelligent reading and teaching of the Manual of Dialectical Thought Forms (DTFM), which in the near future will become available in pdf form on this website under Publications. The article introduces cutting-edge thinking tools... Read More...